This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Tips & Tricks
General
Here you will find information about general issues concerning the operation of the RepRap Industrial in your specific work environment.
Commandline Access to the linux operating system via SSH
Use SSH on your computer connected to the same LAN as your 3D printer to log in to the RepRap Industrials' built-in BeagleBone Black. You can use the hostname from the printers' Backend-URL and log in with the following access data:
User: kiosk Password: eight-digit combination from the serial number at the back of the device. Take the first two four-digit blocks - XX-AAAA-BBBB-CCCC-YYYY becomes an "AAAABBBB" password.
Setting a static IP address for RepRap Industrial ethernet connection
First, establish a commandline connection to the printer.
From within the terminal session, edit the network configuration via the command line editor “nano”
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces (use the same password as for the SSH connection)
The current DHCP setup looks like:
# The primary network interface auto eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp pre-up iptables-restore </etc/iptables.rules
Change the setup according to your needs. Example:
# The primary network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.1.20
netmask 255.255.2555.0
network 192.468.1.0
broadcast 192.168.1.255
gateway 192.168.1.254
dns-search family.local
dns-nameservers 192.168.1.254
pre-up iptables-restore </etc/iptables.rules
The rest of the file remains unchanged. Save the file using CTRL+X and confirm the overwrite query with “Y”. Disconnect and finish by typing
exit
Shut down (see Manual control) and reboot (power-on button, 11 in fig. 4) the RepRap Industrial to establish the alterations.
Use a custom NTP server for time signals
First, establish a commandline connection to the printer.
From within the terminal session, stop the NTP daemon background process
sudo service ntp stop (use the same password as for the SSH connection)
Edit the NTP daemon configuration via the command line editor “nano”
sudo nano /etc/ntp.conf
Search for the few lines beginning with
server ...
and add an additional new line before these with the address to your local NTP server like this
server 192.168.1.123
add another additional statement anywhere in this file
# ignore panic threshold for huge time differences tinker panic 0
The rest of the file remains unchanged. Save the file using CTRL+X and confirm the overwrite query with “Y”.
Re-enable NTP client service for background operation
sudo service ntp start
Disconnect and finish by typing
exit
Shut down (see Manual control) and reboot (power-on button, 11 in fig. 4) the RepRap Industrial to establish the alterations.
Changing Shell Password in the BeagleBone Black Operating System
After manually creating a new Micro-SD Card from a pre-packaged upgrade release provided by Kühling&Kühling, the user account running the RepRapOnRails software in the Linux operating system will be in default configuration. To change the password, use SSH on your computer connected to the same LAN as your 3D printer to log in to the BeagleBone Black. You can use the hostname in the printers' Backend-URL as its address and log in with the following access data:
User: kiosk Password: kiosk
Now you can set a new password by entering
passwd
and following the instructions. In delivery condition the unique password is an eight-digit combination from the serial number at the back of the device. Take the first two four-digit blocks (example: XX-AAAA-BBBB-CCCC-YYYY becomes an “AAAABBBB” password).
Slicing
Any information we gather related to improving or easing the slicing process is listed in the following paragraphs.
Profile display problems in Slic3r for Windows
This bug will be fixed with the upcoming release of SLic3r v1.2.x.
It is a known problem that in Slic3r for Windows the drop-down lists for the profile selection are too narrow to display the full profile name. This can make it impossible to choose the correct profile when processing your slicing settings for creating a G-code.
Try the following to bypass the problem:
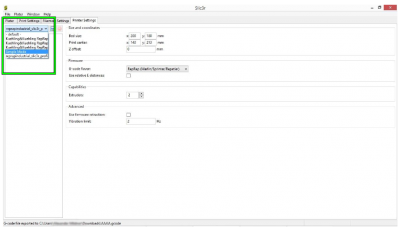
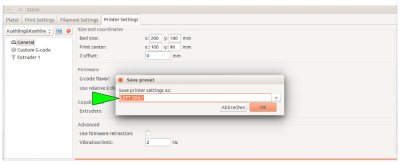
- Select a profile from the drop-down list and click the <save> symbol.
This way, you make the profile name visible and editable.
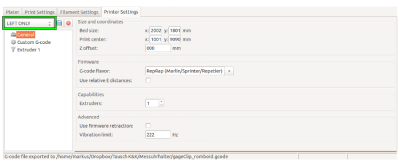
- Delete the current profile name and replace it with a short description, e.g. “LEFT ONLY” instead of “Kuehling&Kuehling RepRap Industrial - LEFT EXTRUDER ONLY”.
Overhang - adjusting the layer thickness
If you want to print filigree objects with overhanging structures without adding supports, try reducing the layer thickness for this print by 15 - 20%. This will result in a finer Z-axis resolution and increased overlay of subsequent layers so that more stability is gained over the height of the target object.
Modifying infill and perimeters
There are currently two Slic3r profiles available at our GitHub repository that provide preset ready-to-print slicing settings. Her are some tips for handling these profiles to adjust them to your needs.
The SOLID profile normally needs no modification since it comes with stable, reliable settings for printing solid objects with 100 % infill.
The ECO profile supplies settings for objects with loosened infill. This makes objects lighter and reduces the print time and the material consumption. To achieve good results, the settings may have to be adjusted.
We recommend to set the following always for printing ECO objects:
- A hull thickness of 1.0 to 1.5 mm. As a rule of thumb divide the hull thickness by the nozzle tip diameter and set the amount of perimeters equal to the result. Such, a closed, smooth and stable hull is ensured.
- Honeycomb infill as it provides highest stability at optimal density.
- A minimum infill of 15 %.
- A maximum infill of 30 %. Increasing the infill further does not have a significant advantage compared to a solid body but strongly increases the printing time.
Operation
In the following you will find more detailed descriptions of functions of the RepRap Industrial. In most cases, these are topics upraised by support requests or in-house lab experiments.
Calibrating the extrusion
The stability and dimensional accuracy of any printed object require a correct amount of filament conveyed through the nozzle. Too little extrusion and the part will be thin-walled, fragile and likely to break. Too much material is likely to clog the nozzle and ruin the print. The amount of material effectively conveyed through the nozzle is depending on:
- the 3D printer itself - slight variations are possible due to the manufacturing process;
- the actual filament diameter - in the range of the dimensional stability of the filament;
- the printed material's properties - the extruder drive wheel grinds deeper into softer materials, thus reducing the actual diameter;
- the idler tension - high tension will cause the drive wheels teeth to grind deeply into the filament, causing a dilation of the material and a reduced output.
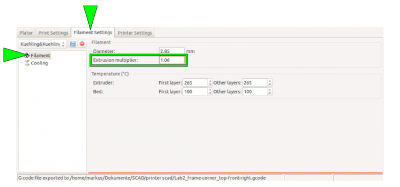
To make sure that the print result is stable and accurate, an extrusion multiplier must be found for every material on every apparatus; it may be that this factor must be found for every spool of filament.
The correct extrusion multiplier is set in the slicing software, compensating for the above named variables.
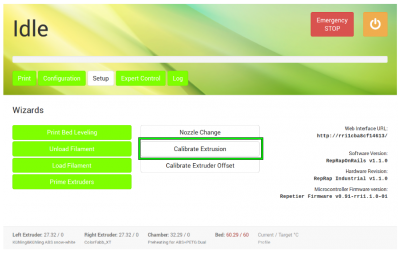
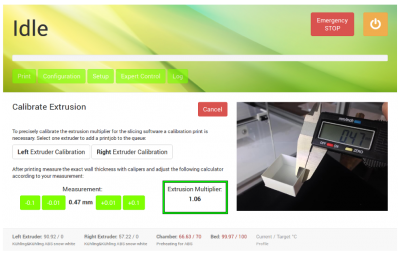
To find the correct multiplier, open the Setup menu at the GUI and choose [Calibrate Extrusion].
A detailed description for ABS filament can be found here.
For other materials, the same procedure applies but you have to prepare a G-code for the test print.
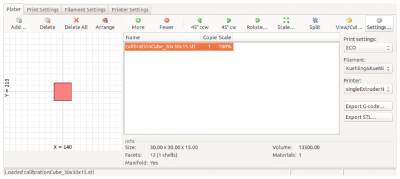
To create a G-code for the extrusion calibration, you need an stl-file of a cube with the dimensions 30x30x15 mm (download here).
Load the stl-file in Slic3r and select the Print Settings tab.
Choose the SOLID profile as a basis.
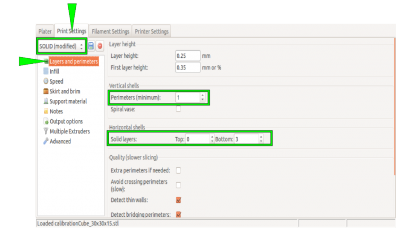
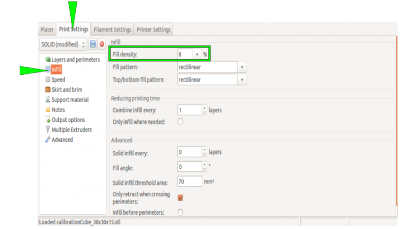
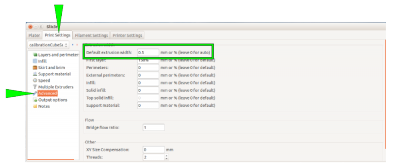
Choose the following settings to make the cube a box without a lid and only one perimeter of 0.5 mm thickness for a wall:
| Layers and Perimeters → Vertical shells Perimeters (minimum) | 1 |
| Layers and Perimeters → Horizontal shells Solid Layers TOP | 0 |
| Layers and Perimeters → Horizontal shells Solid Layers BOTTOM | 3 |
| Infill → Fill density | 0 % |
| Advanced → Default extrusion width | 0.5 |
INFO
Saving these settings as an “extruder calibration” profile will make this calibration much more comfortable in the future.
Upload the G-code to your 3D printer, print it, measure the wall thicknesses, and calculate the mean value.
Then open the [Calibrate Extrusion] wizard and enter the mean value.
Deactivating the heating elements after end of print job
Sometimes you may want to start a print job just before finishing time or the weekend. Since there is currently no automatic shutdown function, the 3D printer will then stay on all night respectively some days. With the following description you can alter the End G-code of your print so that the heating elements are shut off after the print job has been finished so that the power consumption is reduced significantly. A side effect is, that due to the fact that the build chamber needs some hours to channel off the heat the cooling process is slowed and thereby internal tensions of the printed object are reduced. To deactivate the heating elements after a print job:
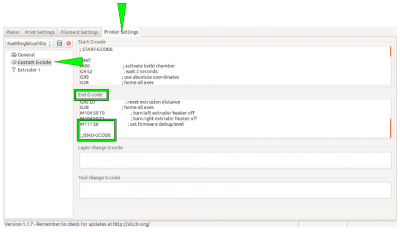
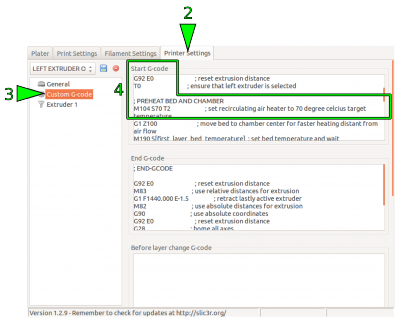
- Open the [Printer Settings] tab in Slic3r and choose the Custom G-code menu.
- Activate the End G-code editor by clicking into the text field.
- Position the cursor in the last line before the
; /END-GCODEentry. - Enter the command
M104 S0 T2
This will set the heating elements of the build chamber to a temperature of 0 °C. - Enter the command
M140 S0
This will deactivate the print bed as the last action of the current G-code.
Adjusting the build chamber temperature
NOTICE
The build chamber temperature is preset to the maximal permissible temperature of +70 °C at delivery.
Exceeding +70 °C will damage interior components of the RepRap Industrial such as stepper motors, bearings and electronics.
Since hitherto the RepRap Industrial is the only commercially available Open Source 3D printer with an actively heated build chamber, common slicing software does not feature ambient temperature settings. For some materials, it is advantageous to modify the chamber temperature together with the other temperature settings. The build chamber's temperature of the RepRap Industrial is set via the “Start G-code” which can be manually altered.
To change the build chamber temperature (in the following example we use our standard Slic3r - other software may differ in denotations):
- Open your slicing software.
- Open the tab “Printer Settings” and choose “Custom G-code”.
Go to the line reading:
M104 S70 T2; set recirculating air heater to 70 degree celcius target temperature
- Change the entry “Sxy” (here S70) by replacing the value xy with the desired temperature, for example 50° C:
M104 S50 T2; set recirculating air heater to 50 degree celcius target temperature
(for logical reasons, the comment should be aligned)
- If you want to keep the settings, save them in the profile (see Slic3r manual).
Any G-code exported with this profile loaded will heat the build chamber to the stated temperature prior to printing.
G-code manipulation at the GUI
The following list contains supported G-code commands that can be used on demand to directly interfere with a print procedure or setting via the G-code keyboard of the GUI's Log menu.
| Command | Effect | Example |
|---|---|---|
G1 | Coordinated Movement X Y Z E | G1 X130 Y85 Z1.75 E4.35 |
G4 S<seconds> | Wait for given duration in seconds | G4 S5 (waits 5 seconds) |
G28 | Home all axes | |
G90 | Use absolute coordinates | |
G91 | Use relative coordinates | |
M80 | Activate build chamber | |
M82 | Set E codes absolute (default) | |
M83 | Set E codes relative while in Absolute Coordinates (G90) mode | |
M104 S<temp> T<extruder> | Set temperature without wait | Adjusting the build chamber temperature, Deactivating the heating elements after end of print job |
M109 S<temp> T<extruder> | Set temperature with wait | |
M140 S<temp> | Set bed target temp without wait | |
M190 S<temp> | Set bed target temp with wait | |
M221 S<extrusion flow multiplier in percent> | Increase/decrease given flow rate | M221 S95 → decrease flow to 95 % of g-code value |
M220 S<print speed multiplier in percent> | Increase/decrease print speed of all drive speeds | M220 S95 → decrease print speed to 95 % of g-code value |